The Creyos ADHD Cognitive Assessment and Automated Report
The prevalence of attention deficit hyperactivity disorder...
Read article
Administer the Vanderbilt ADHD diagnostic rating scale questionnaire in Creyos Health on its own or part of the Creyos ADHD Condition-Focused Protocol to understand of patient wellbeing.

Administer the VADRS assessment in person or digitally with automated scoring and reporting for an efficient, patient-friendly experience.

Get access to instant scoring, the complete Creyos ADHD assessment protocol, and trend lines over time—all in one platform.

Gain confidence that all Creyos health assessments are scientifically validated and committed to medical best practices.
Understanding ADHD symptoms and behaviors can be the difference in long-term outcomes. Administer the Vanderbilt ADHD diagnostic rating scale as part of the Creyos ADHD protocol to measure for 14 distinct markers of ADHD.
Source: Harris, E. JAMA. 2024. doi:10.1001/jama.2024.5159

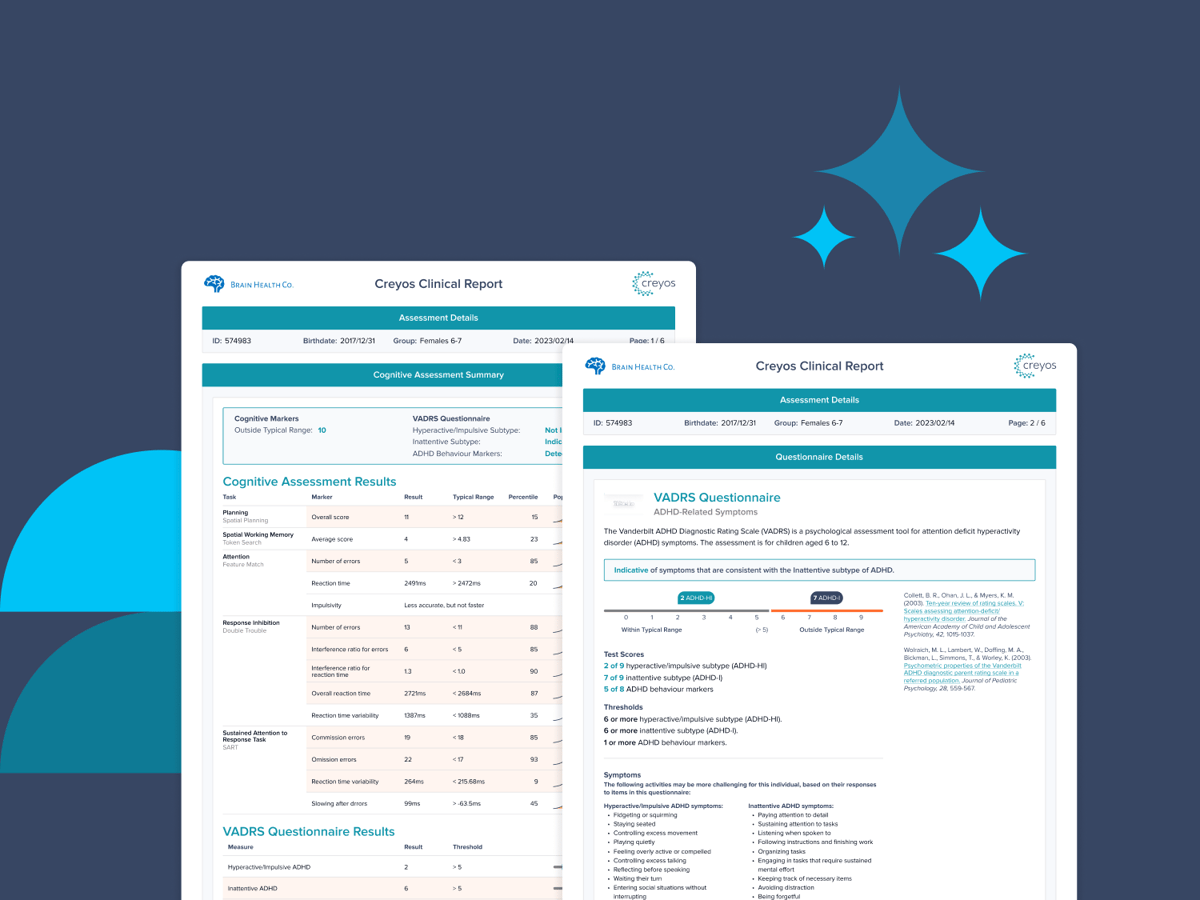
Designed for parents, the Vanderbilt ADHD rating scale offered through Creyos is a 55-question checklist based on the ADHD diagnosis guidelines established in the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders (DSM).
When administered alongside measures of cognitive performance, it allows parents and healthcare providers to:

The VADRS was designed to assess ADHD in children ages 6 to 12 and should be used alongside measures of cognitive function to understand the child’s overall wellbeing.
The VADRS assessment contains 55 questions related to criteria for ADHD, oppositional defiant disorder (ODD), conduct disorder (CD), and criteria from the Pediatric Behavior Scale for anxiety and depression. It can be administered in person through the Creyos Health platform on an in-clinic device or remotely through a provided link.
Creyos Health automatically scores VADRS results and provides reports. Higher scores indicate a greater possibility of ADHD diagnosis.
Healthcare providers can discuss results with patients and combine with other ADHD assessments, cognitive tasks, and longitudinal tracking to build a complete picture of patient health.

Research suggests that children with ADHD often exhibit impairment in their ability to focus, control impulses, and remember information. These cognitive challenges can significantly impact children’s daily lives and academic performance, and are often comorbid with other mental health conditions later in life.
The Vanderbilt ADHD diagnostic rating scale is a vital ADHD assessment tool in the comprehension of ADHD in children over time. In fact, VADRS scores for inattention, hyperactivity, and impulsivity are directly correlated with parent-reported measures of executive function. Learn more about administering the VADRS assessment along with additional ADHD and cognitive functioning tests in Creyos Health.
Source: Becker & Langberg, 2013; Mayer JS et al., 2022
Cognition differences have been linked with ADHD in children. For example, both the inattention and hyperactivity/impulsivity scores on the VADRS are correlated with parent-reported measures of executive function (Becker & Langberg, 2013), and other DSM-based ADHD scales have been linked with intellectual function (e.g., children diagnosed with predominantly inattentive ADHD tend to score lower in the processing speed index of the WISC-IV; Thaler, Bello, & Etcoff, 2012).
When treating ADHD, cognition has been used as a key outcome measure to gauge progress and adjust intervention plans. In one study, children enrolled in a behavioural program for treating attentional issues improved on Creyos Health measures of cognition more than a control group (Jackson & Wild, 2021), and the cognitive reports have been used to objectively demonstrate progress to parents.
For medication-based treatments such as methylphenidate, objective cognitive measures complement parent rating forms to help determine proper dosages and measure progress. In fact, cognition may mediate the effects of medication on behavioural outcomes such as productivity—that is, medication improves cognition, which goes on to improve visible symptoms of ADHD (see Hawk et al., 2018). Measuring cognition may also be beneficial for long-term follow up with ADHD patients, as maturation of cognitive function can predict ADHD remission (Halperin et al., 2008; Karalunas et al., 2017).
The VADRS assessment evaluates behaviors related to ADHD in children ages 6 to 12, including inattention (difficulty focusing, staying organized, and following through on tasks), hyperactivity (excessive energy, restlessness, and fidgeting), and impulsivity (acting without thinking, interrupting others, and difficulty waiting).

The prevalence of attention deficit hyperactivity disorder...
Read article

According to the CDC, almost 1 in 10 children will be...
Read article

According to a 2019 review, 60–90% of children with...
Read article