
What is the IADL Measure for Assessing Cognitive Decline?
Daily living can be the most challenging cognitive task of...
Read article
Measuring instrumental activities of daily living (IADLs) in Creyos Health helps providers understand a patient’s ability to perform activities that are essential for independent living.

Overcome technology hesitancy or mobility, vision, or hearing limitations for older patients by offering the IADL questionnaire in clinic or at home.

Offer as part of annual wellness visits and routine testing for older adults to measure independent living regularly and ensure patient safety and wellbeing.

Detect meaningful changes and declines in cognitive health with a centralized patient health record that includes longitudinal data.
Administer the IADL questionnaire as part of Creyos’ complete dementia protocol to quantify patient independence and guide decisions about treatment, living arrangements, or other next steps.
Review our guide below for a complete look at the Creyos Dementia Assessment protocol.

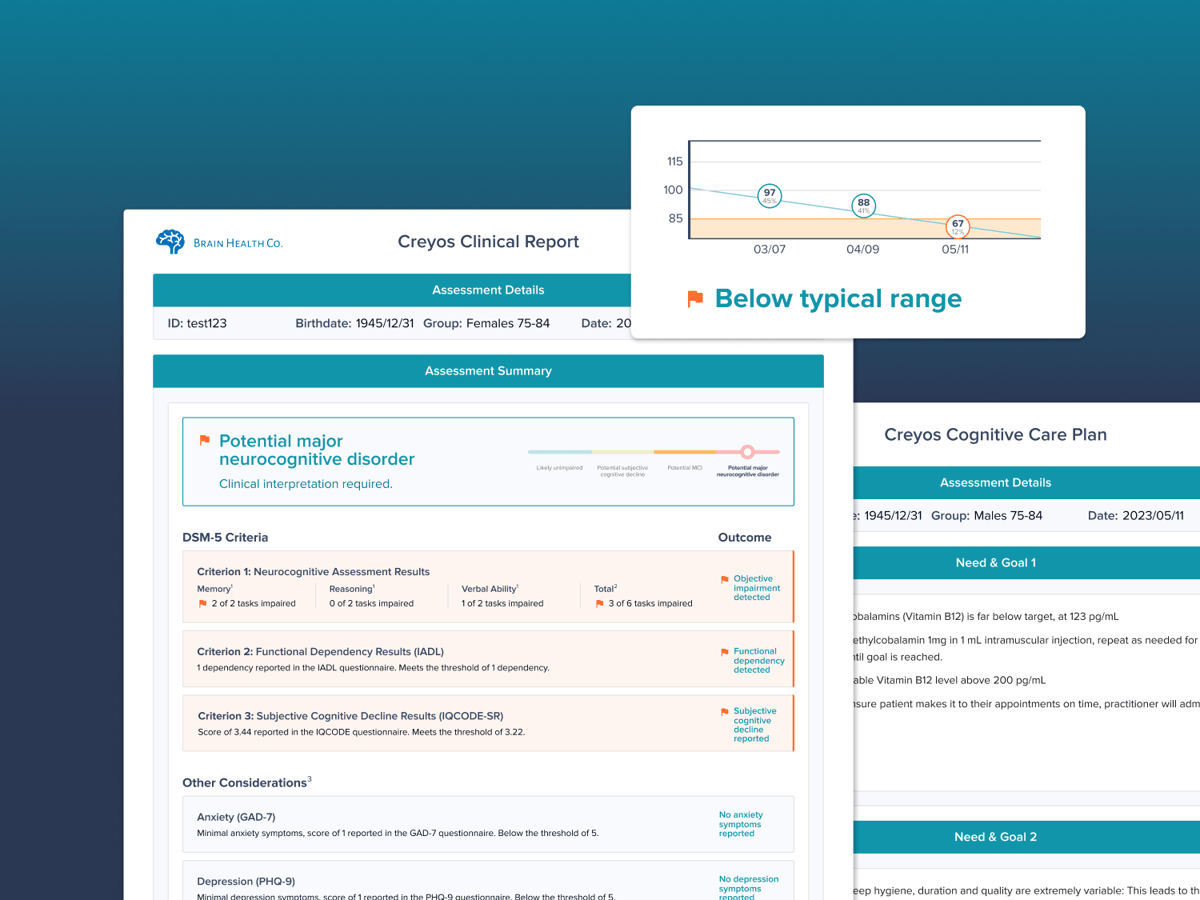
Deficits revealed by the questionnaire are associated with mild cognitive impairment (MCI), and that patients with MCI who exhibit IADL deficits are at a higher risk of converting to dementia. However, assessing IADLs is not without limitations—whether due to biases from self-report or via a caregiver.
Therefore, objective, performance-based measures of cognition are also needed to complement the IADL, identify specific strengths and weaknesses in various domains of cognitive function, and possibly spot cognitive deficits that have not yet translated into an inability to complete complex activities independently.
Source: Jekel et al., 2025
The Instrumental Activities of Daily Living questionnaire offered through Creyos is designed to assess independent living skills.
When administered alongside measures of cognitive performance, it allows clinicians to:

Creyos is committed to improving accessibility for patients with diverse needs. Our platform offers approachable patient onboarding, simplified instructions, multilingual capabilities, inclusive interfaces, and streamlined workflows.
The IADL questionnaire contains a series of questions that rate a patient’s ability to perform various independent living skills. The Creyos Health platform automatically compares caregiver responses side by side with the patient’s.
Creyos Health automatically scores IADL questionnaire results and provides reports. Lower scores indicate a greater degree of dependence on others to carry out daily living tasks.
If the patient requires further cognitive testing or is diagnosed with dementia, providers can offer follow-up assessments or complete cognitive care planning directly in the Creyos Health platform.

Nearly 7 million Americans are living with Alzheimer’s disease, and that number is expected to grow to 13 million by 2050. However, up to 96% of providers are unaware of the best cognitive assessment tools to use in their practice.
The Creyos Health dementia protocol aims to close the gap in cognitive care by giving healthcare providers an end-to-end solution to effectively detect, test, manage, and track cognitive function. Backed by 30 years of rigorous scientific research and aligned to Alzheimer’s Association standards, the toolkit supports more specific diagnosis, sensitive detection, clearly defined comorbid conditions, automated reporting, and better patient outcomes.
Source: Alzheimer’s Association, 2024; Alzheimer’s Association, 2019
Instrumental activities of daily living (or IADLs) are complex tasks that require a combination of physical, cognitive, and social skills. This includes using the telephone, shopping, preparing meals, housekeeping, laundry, transportation, and taking medications.
IADLs are often used as a measure of functional independence, especially among older adults, and difficulty with IADLs can indicate a decline in functional independence and may be a sign of underlying health conditions, such as dementia or stroke.
Studies have generally found that this version of the IADL is reliable over time and across raters (e.g., Edwards, 1990), and is valid for discriminating between people with and without dementia when using a cutoff score of one or more deficits to indicate possible dementia (e.g., Mao et al., 2018).
The Instrumental Activities of Daily Living questionnaire evaluates a patient’s ability to perform activities considered essential to daily life, including using the telephone, shopping, preparing meals, housekeeping, laundry, transportation, and taking medications.

Daily living can be the most challenging cognitive task of...
Read article
Accurate dementia detection is more important than ever....
Read article

Cognitive decline is on the rise as the aging U.S....
Read article